Using the Trento MCP Server
The Trento MCP Server provides the interface for AI-assisted infrastructure operations, enabling agentic assistants to integrate with Trento. By utilizing the Model Context Protocol, these assistants can perform monitoring and troubleshooting tasks through natural language. See MCPHost on SLES or Using alternative MCP clients for details.
Integrating the Trento MCP Server with MCPHost
This guide explains how to connect the Trento MCP Server to SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 16 using MCPHost, a lightweight CLI tool for the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
|
Supported only on SUSE Linux Enterprise Server for SAP applications 16.0 |
Prerequisites
-
An LLM provider and credentials.
-
Public hosted options, such as Google Gemini, OpenAI, etc.
-
Private/on-premises option, such as SUSE AI.
-
-
A running Trento Server installation with the Trento MCP Server component enabled.
-
A Trento Personal Access Token generated in Trento Web Profile view.
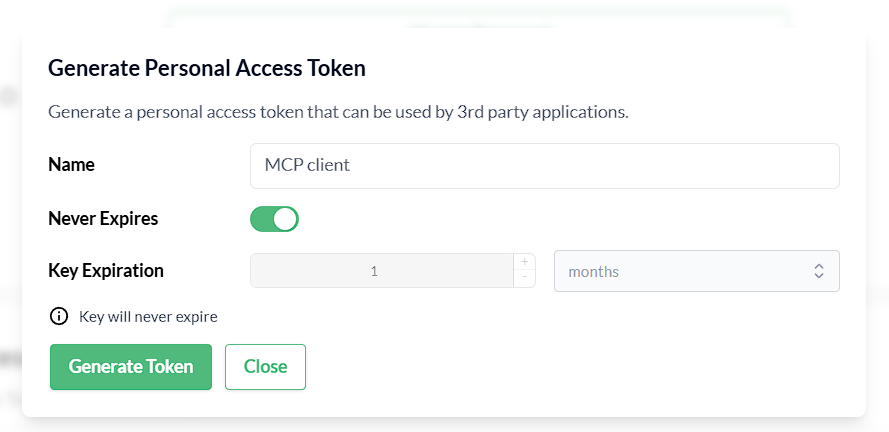 Figure 1. Generate a Personal Access Token in Trento
Figure 1. Generate a Personal Access Token in Trento
Install MCPHost
To install MCPHost, open a terminal and run the following commands:
sudo zypper refresh
sudo zypper install mcphostAfter installation, verify that MCPHost is available and working by checking its version:
mcphost --versionConfigure MCPHost
MCPHost reads its configuration from several locations; one common location is ~/.mcphost.yml. Create ~/.mcphost.yml with the following content:
mcpServers:
trento-mcp-server:
type: "remote"
url: https://trento.example.com/mcp-server-trento/mcp
headers:
- "Authorization: Bearer ${env://TRENTO_PAT}"-
Replace
https://trento.example.com/mcp-server-trento/mcpwith the actual URL where your Trento MCP Server is accessible:-
For Kubernetes deployments with ingress, use the ingress URL (e.g.,
https://trento.example.com/mcp-server-trento/mcp). -
For local or development setups, use
http://localhost:5000/mcp(adjust the port as needed). -
The transport type is configured on the Trento MCP Server, if using Server-Sent Events (SSE) transport instead of the default streamable transport, change the path from
/mcpto/sse.
-
-
If you configured a custom header name (using
HEADER_NAMEor--header-name), updateAuthorizationaccordingly.
|
Security best practice: Keep secrets out of configuration files. Store your keys in environment variables instead of hardcoding them. Export your keys in the shell before running MCPHost. For example: |
|
Configure remote LLM models directly in your MCPHost configuration. For example, to use Google Gemini as your model provider: |
Run MCPHost and use Trento tools
-
Start MCPHost:
mcphostIf no servers appear on startup, confirm your configuration file exists at
~/.mcphost.ymland that your environment variables are exported in the same shell session. -
Verify the connection to Trento and basic status:
/servers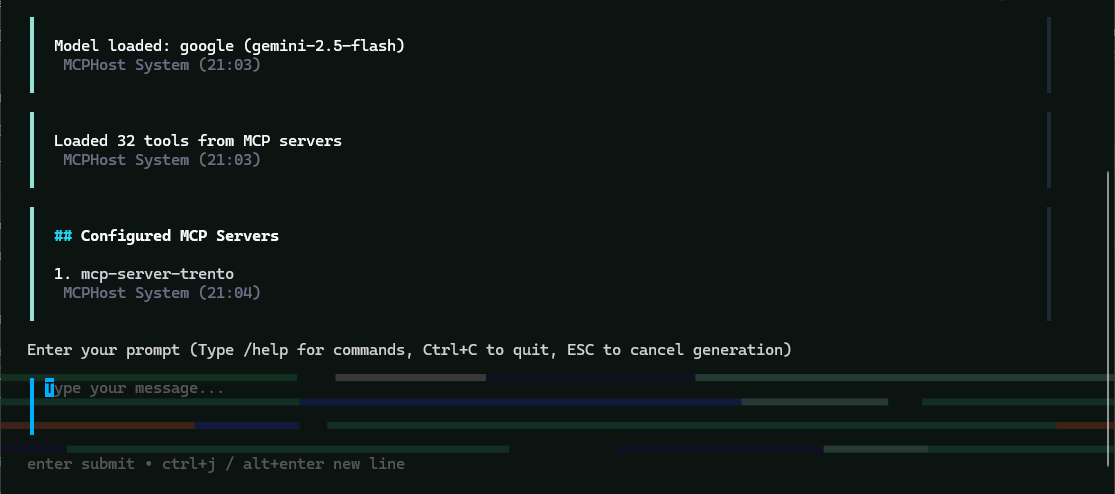 Figure 2. MCPHost initial screen with the Trento MCP Server connected
Figure 2. MCPHost initial screen with the Trento MCP Server connected
Use MCPHost to interact with Trento Server
-
"List all SAP systems managed".
-
"Show my HANA clusters".
-
"Are my SAP systems compliant?"
-
"What is the health status of my SAP landscape?"
-
"Show me all hosts running SAP applications".
-
"Are there any critical alerts I need to address?"
-
"Get details about the latest check execution results".
-
"Which SAP systems are currently running?"
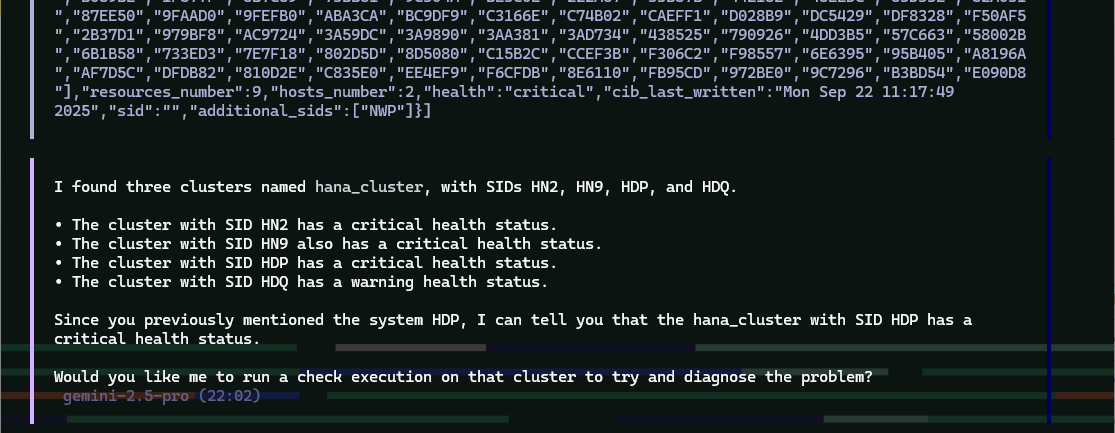
Example MCPHost session querying Trento about SAP systems:
MCPHost Troubleshooting
If you encounter issues connecting MCPHost to the Trento MCP Server:
-
Connection errors
-
Verify that the Trento MCP Server URL in
~/.mcphost.ymlis correct and accessible from your system. -
Check if the Trento MCP Server is running by reviewing logs from your Trento installation.
-
Ensure network connectivity and that any required firewall rules are in place.
-
Test basic connectivity:
curl -I https://trento.example.com/mcp-server-trento/mcp.
-
-
Authentication errors
-
Verify that your personal access token is valid by testing it directly with your Trento Server API.
-
Ensure
TRENTO_PATis exported in the same shell session before runningmcphost. -
Check that the header name matches your server configuration (default:
Authorization). -
Ensure the token has the necessary permissions in Trento.
-
-
LLM provider errors
-
Verify that LLM
GOOGLE_API_KEY(or your provider’s API key) is exported correctly. -
Check the
provider-urlandmodelconfiguration in your~/.mcphost.yml. -
Confirm that your API key has sufficient quota and permissions with your provider.
-
-
General issues
-
Check the MCPHost terminal output for detailed error messages during startup or operation.
-
Review the Trento MCP Server logs for connection attempts and errors.
-
Verify that your configuration file exists at
~/.mcphost.ymland has correct YAML syntax.
-
Integrating the Trento MCP Server with other clients
The Trento MCP Server can be integrated with any client application that supports the Model Context Protocol. This makes it possible to interact with the Trento API and execute tools defined in the OpenAPI specification through your preferred AI assistant or development tool.
This guide uses Visual Studio Code with GitHub Copilot as an example, but the configuration procedures apply to any MCP-compatible client.
Prerequisites
-
An LLM provider and credentials.
-
Public hosted options, such as Google Gemini, OpenAI, etc.
-
Private/on-premises option, such as SUSE AI.
-
-
A running Trento Server installation with the Trento MCP Server component enabled.
-
A Trento Personal Access Token generated in Trento Web Profile view.
 Figure 3. Generate a Personal Access Token in Trento
Figure 3. Generate a Personal Access Token in Trento
Configuring your client
Once you have your Trento Server installation ready with the Trento MCP Server URL and API token, you can configure the MCP Server client. The examples below show JSON configuration format used by most MCP Server clients, including VS Code, Claude Desktop, and others.
Option 1: Configuration with prompted input
This configuration asks for your personal access token when the client starts, keeping credentials secure and out of configuration files. The password: true setting ensures your personal access token input is masked when you type it.
|
This option is supported by most clients, including VS Code. Check your client’s documentation if the prompt feature is not available. |
{
"servers": {
"trento": {
"type": "http",
"url": "https://trento.example.com/mcp-server-trento/mcp",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "${input:trento-personal-access-token}"
}
}
},
"inputs": [
{
"type": "promptString",
"id": "trento-personal-access-token",
"description": "Trento API key",
"password": true
}
]
}Option 2: Direct header configuration
For clients that don’t support prompted input, or for testing purposes, set your Trento personal access token directly in the configuration file.
|
When using this option, ensure your configuration file has appropriate permissions and is not committed to version control systems. |
{
"servers": {
"trento": {
"type": "http",
"url": "https://trento.example.com/mcp-server-trento/mcp",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "trento-personal-access-token"
}
}
}
}|
Replace |
Client options
For detailed guidance on taking advantage of MCP capabilities in different tools, refer to the following official documentation:
-
Visual Studio Code with GitHub Copilot - MCP Server Configuration.
-
Cursor - AI-powered code editor with MCP support.