MCP Integration
The Trento MCP Server is an optional component that enables AI-assisted infrastructure management for your SAP landscape. It exposes Trento functionality through the Model Context Protocol (MCP), an open standard that facilitates secure communication between data sources and AI agents. While the core Trento Server operates independently, the Trento MCP Server component allows you to integrate Trento into an agentic AI workflow. This enables the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) to perform common monitoring and troubleshooting tasks using natural language, providing a standardized way for AI tools to access real-time system state and best-practice validations.
Installing Trento MCP Server
The Trento MCP Server can be deployed in different ways depending on your infrastructure and requirements.
Supported installation methods:
Prerequisites Trento MCP Server
The Trento MCP Server is lightweight and stateless. No persistent storage is required; allocate space for logs as per your logging policy. Before installing the Trento MCP Server, both Trento Web and Trento Wanda components must be running and be accessible for the Trento MCP Server to function properly.
-
There must be network connectivity between the Trento MCP Server and Trento Server components.
-
Access to the Trento Server URL (important when deployed behind NGINX, or any other reverse proxy) must be possible.
Kubernetes deployment of Trento MCP Server
The subsection uses the following placeholders:
-
TRENTO_SERVER_HOSTNAME: the host name used by the end user to access the console. -
ADMIN_PASSWORD: the password of the admin user created during the installation process.The password must meet the following requirements:
-
minimum length of 8 characters
-
the password must not contain 3 identical numbers or letters in a row (for example, 111 or aaa)
-
the password must not contain 4 sequential numbers or letters (for example, 1234, abcd, ABCD)
-
Enable the Trento MCP Server
When installing Trento Server following the instructions in [sec-trento-k8s-deployment], the Trento MCP Server is disabled by default. Enable it by passing --set trento-mcp-server.enabled=true:
helm upgrade --install trento-server oci://registry.suse.com/trento/trento-server \
--set global.trentoWeb.origin=TRENTO_SERVER_HOSTNAME \
--set trento-web.adminUser.password=ADMIN_PASSWORD \
--set trento-mcp-server.enabled=trueThe Trento MCP Server will automatically connect to the Trento Web and Trento Wanda internal services within the Kubernetes cluster.
Verify the Trento MCP Server installation
-
Check that the Trento MCP Server Pod is running:
kubectl get pods -l app.kubernetes.io/name=mcp-serverExample output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE trento-server-mcp-server-xxxxxxxxxx-xxxxx 1/1 Running 0 2m -
Check the logs:
kubectl logs -l app.kubernetes.io/name=mcp-server -
Check the Trento MCP Server health endpoints:
# Expose the health check port from the Pod, as it is not exposed as a Kubernetes Service. kubectl port-forward --namespace default \ $(kubectl get pods --namespace default -l app.kubernetes.io/name=mcp-server -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}") \ 8080:8080While the previous command is running, perform the following check:
# Liveness endpoint: curl http://localhost:8080/livez# Readiness endpoint: curl http://localhost:8080/readyzExample output:
# Liveness: {"info":{"name":"trento-mcp-server","version":"0.1.0"},"status":"up"} # Readiness: {"status":"up","details":{"mcp-server":{"status":"up","timestamp":"2025-10-09T12:11:09.528898849Z"},"wanda-api":{"status":"up","timestamp":"2025-10-09T12:11:09.544855047Z"},"web-api":{"status":"up","timestamp":"2025-10-09T12:11:09.544855047Z"}}}
Trento MCP Server Helm configuration options
The Trento MCP Server Helm chart supports various configuration options:
Customize Ingress Path
By default, ingress is enabled. To customize the ingress configuration in a basic K3s installation, run the command below:
helm upgrade --install trento-server oci://registry.suse.com/trento/trento-server \
--set global.trentoWeb.origin=TRENTO_SERVER_HOSTNAME \
--set trento-web.adminUser.password=ADMIN_PASSWORD \
--set trento-mcp-server.enabled=true \
--set trento-mcp-server.ingress.hosts[0].host=TRENTO_SERVER_HOSTNAME \
--set trento-mcp-server.ingress.hosts[0].paths[0].path=/mcp-server-trento \
--set trento-mcp-server.ingress.hosts[0].paths[0].pathType=ImplementationSpecificThe Trento MCP Server endpoint will be: https://TRENTO_SERVER_HOSTNAME/mcp-server-trento/mcp
Adjust Log Verbosity
The default log level is info. Adjust it for debugging:
helm upgrade --install trento-server oci://registry.suse.com/trento/trento-server \
--set global.trentoWeb.origin=TRENTO_SERVER_HOSTNAME \
--set trento-web.adminUser.password=ADMIN_PASSWORD \
--set trento-mcp-server.enabled=true \
--set trento-mcp-server.mcpServer.verbosity=debugAdjust Resource Limits
For production deployments with different resource requirements:
helm upgrade --install trento-server oci://registry.suse.com/trento/trento-server \
--set global.trentoWeb.origin=TRENTO_SERVER_HOSTNAME \
--set trento-web.adminUser.password=ADMIN_PASSWORD \
--set trento-mcp-server.enabled=true \
--set trento-mcp-server.resources.requests.cpu=100m \
--set trento-mcp-server.resources.requests.memory=128Mi \
--set trento-mcp-server.resources.limits.cpu=1000m \
--set trento-mcp-server.resources.limits.memory=1GiDisabling Health Check Probes
Health check probes are enabled by default. To disable them if needed, run the following command:
helm upgrade --install trento-server oci://registry.suse.com/trento/trento-server \
--set global.trentoWeb.origin=TRENTO_SERVER_HOSTNAME \
--set trento-web.adminUser.password=ADMIN_PASSWORD \
--set trento-mcp-server.enabled=true \
--set trento-mcp-server.livenessProbe.enabled=false \
--set trento-mcp-server.readinessProbe.enabled=falseComplete configuration example
Below is a complete example that configures external access via a custom ingress path:
helm upgrade --install trento-server oci://registry.suse.com/trento/trento-server \
--set global.trentoWeb.origin=https://trento.example.com \
--set trento-web.adminUser.password=SecurePassword123 \
--set trento-mcp-server.enabled=true \
--set trento-mcp-server.mcpServer.trentoURL=https://trento.example.com \
--set trento-mcp-server.ingress.hosts[0].host=trento.example.com \
--set trento-mcp-server.ingress.hosts[0].paths[0].path=/mcp-server-trento \
--set trento-mcp-server.ingress.hosts[0].paths[0].pathType=ImplementationSpecificsystemd deployment
A systemd-based installation of the Trento MCP Server using RPM packages can be performed manually on the latest supported versions of SUSE Linux Enterprise Server for SAP applications.
Supported versions:
-
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server for SAP applications 15: SP4–SP7
-
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server for SAP applications 16.0
Installing Trento MCP Server using RPM packages
-
Install the Trento MCP Server package:
zypper install mcp-server-trento
Configure Trento MCP Server
-
Create the Trento MCP Server configuration file
/etc/trento/mcp-server-trentoby copying the example:cp /etc/trento/mcp-server-trento.example /etc/trento/mcp-server-trento -
Edit the configuration file to point to your Trento Server:
vim /etc/trento/mcp-server-trentoExample configuration:
AUTODISCOVERY_PATHS=/api/all/openapi,/wanda/api/all/openapi ENABLE_HEALTH_CHECK=false HEADER_NAME=Authorization HEALTH_API_PATH=/api/healthz HEALTH_PORT=8080 # OAS_PATH=https://trento.example.com/api/all/openapi,https://trento.example.com/wanda/api/all/openapi PORT=5000 TAG_FILTER=MCP TRANSPORT=streamable TRENTO_URL=https://trento.example.com VERBOSITY=info INSECURE_SKIP_TLS_VERIFY=false
Configure the Trento MCP Server using either TRENTO_URL or OAS_PATH.
If OAS_PATH is left empty, the Trento MCP Server automatically discovers the APIs from the Trento Server using TRENTO_URL.
If OAS_PATH is set, it takes precedence and TRENTO_URL is ignored.
Use TRENTO_URL when one or more of the following conditions apply:
-
Trento Server is deployed behind a reverse proxy (NGINX, etc.).
-
The Trento MCP Server runs on a different host or network than Trento Server.
-
You want to use external or public URLs.
-
You prefer automatic API autodiscovery.
Use OAS_PATH when one or more of the following conditions apply:
-
You want to connect directly to internal services without autodiscovery.
-
You need to bypass reverse proxy configurations.
Verify the Trento MCP Server service
-
Verify the service is running:
systemctl status mcp-server-trentoExpected output:
● mcp-server-trento.service - Trento MCP Server service Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/mcp-server-trento.service; enabled) Active: active (running) since ... -
Check the service logs:
journalctl -u mcp-server-trento -f -
If firewalld is running, allow Trento MCP Server to be accessible and add an exception to firewalld:
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=5000/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --reload -
If you enabled health checks and want to expose them, also allow the health check port:
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --reload -
If you enabled health checks, verify the endpoints locally:
# Note: Replace localhost with the server's IP/hostname if running these commands from a remote machine, # and ensure the health port is allowed by your firewall. # Liveness endpoint: curl http://localhost:8080/livez # Example output: # {"info":{"name":"trento-mcp-server","version":"0.1.0"},"status":"up"} # Readiness endpoint: curl http://localhost:8080/readyz # Example output: # {"status":"up","details":{"mcp-server":{"status":"up","timestamp":"2025-10-09T12:11:09.528898849Z"},"wanda-api":{"status":"up","timestamp":"2025-10-09T12:11:09.542078327Z"},"web-api":{"status":"up","timestamp":"2025-10-09T12:11:09.544855047Z"}}}
Configuring Trento MCP Server
This section provides an overview of how to configure the Trento MCP Server depending on the deployment method.
Configuration in a Kubernetes deployment
Configuration Sources
The Trento MCP Server supports multiple configuration sources with the following priority order (highest to lowest):
-
Environment variables - Used for containerized deployments.
-
Built-in defaults - Fallback values.
Configuration Overview
| Environment Variable | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Custom paths for API autodiscovery. |
|
|
Enable the health check server. |
|
(empty) |
Configuration file path. |
|
|
Header name used to pass the Trento API key to the Trento MCP Server. |
|
|
API path used for health checks on target servers. |
|
|
Port where the health check server runs. |
|
|
Skip TLS certificate verification when fetching OAS specs from HTTPS. |
|
|
Path(s) to OpenAPI specification file(s). Can be set multiple times. |
|
|
Port where the Trento MCP Server runs. |
|
|
Only include operations that contain one of these tags. |
|
|
Protocol to use: |
|
(empty) |
Target Trento server URL. Required for autodiscovery if OAS path is not set. |
|
|
Log level: |
Kubernetes Deployment Example
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mcp-server-trento
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: mcp-server-trento
image: mcp-server-trento:latest
env:
- name: TRENTO_MCP_PORT
value: "5000"
- name: TRENTO_MCP_HEALTH_PORT
value: "8080"
- name: TRENTO_MCP_ENABLE_HEALTH_CHECK
value: "true"
- name: TRENTO_MCP_TRENTO_URL
value: "https://trento.example.com"
- name: TRENTO_MCP_VERBOSITY
value: "info"
ports:
- containerPort: 5000
name: mcp
- containerPort: 8080
name: healthConfiguration in an systemd deployment
Configuration Sources
The Trento MCP Server supports multiple configuration sources with the following priority order (highest to lowest):
-
Command-line flags - Override config for the current process.
-
Configuration file - Persistent settings configuration.
Configuration Overview
The mcp-server-trento binary accepts several command-line flags to configure its behavior. The following table lists all available configuration options, their corresponding flags, configuration variables, and default values.
| Flag | Config Variable | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Custom paths for API autodiscovery. |
|
(empty) |
(empty) |
Configuration file path. |
|
|
|
Enable the health check server. |
|
|
|
Header name used to pass the Trento API key to the Trento MCP Server. |
|
|
|
API path used for health checks on target servers. |
|
|
|
Port where the health check server runs. |
|
|
|
Skip TLS certificate verification when fetching OAS specs from HTTPS. |
|
|
|
Path(s) to OpenAPI specification file(s). Can be set multiple times. |
|
|
|
Port where the Trento MCP Server runs. |
|
|
|
Only include operations that contain one of these tags. |
|
|
|
Protocol to use: |
|
|
(empty) |
Target Trento server URL. Required for autodiscovery if OAS path is not set. |
|
|
|
Log level: |
Configure Trento MCP Server with Command-Line Flags
Trento MCP Server allows you to override configuration settings using command-line flags for temporary changes. These overrides are not persistent and are lost when the process stops or the system is rebooted. To make configuration changes permanent for the systemd service, update /etc/trento/mcp-server-trento and restart the service.
Basic usage with custom port, verbosity, and target URL:
mcp-server-trento --port 9000 --verbosity debug --trento-url https://trento.example.comUsing multiple OpenAPI specifications:
mcp-server-trento --oas-path https://api1.example.com/openapi.json --oas-path https://api2.example.com/openapi.jsonAutodiscovery with custom paths:
mcp-server-trento --trento-url https://trento.example.com --autodiscovery-paths /api/v1/openapi,/wanda/api/v1/openapiEnable health checks on a custom port:
mcp-server-trento --enable-health-check --health-port 8080 --port 5000Health Check Configuration
The Trento MCP Server includes built-in health check endpoints for systemd and Kubernetes integration.
|
Health check functionality is disabled by default and must be explicitly enabled using the |
Health Check Endpoints
The health check server provides the following endpoints:
-
/livez- Liveness probe for Kubernetes pod restart decisions. -
/readyz- Readiness probe for traffic routing decisions.
The readiness endpoint performs comprehensive health checks, including:
-
mcp-server- Validates Trento MCP Server connectivity using an MCP client. -
api-server- Verifies connectivity to the configured Trento API server.
Enable Health Checks with Helm on a Kubernetes deployment
Enable health checks when deploying on Kubernetes with Helm:
helm upgrade \
--install trento-server oci://registry.suse.com/trento/trento-server \
--set global.trentoWeb.origin=TRENTO_SERVER_HOSTNAME \
--set trento-web.adminUser.password=ADMIN_PASSWORD \
--set trento-mcp-server.enabled=true \
--set TRENTO_MCP_ENABLE_HEALTH_CHECK=true \
--set TRENTO_MCP_HEALTH_PORT=8080The health port is internal to the Kubernetes cluster. To reach it from the host running Kubernetes, forward the Pod port. Replace NAMESPACE with your target namespace (Helm defaults to default).
kubectl port-forward --namespace NAMESPACE \
$(kubectl get pods --namespace NAMESPACE -l app.kubernetes.io/name=mcp-server -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}") \
8080:8080 &With the port forward active, test the endpoints in Testing Health Endpoints.
Enable Health Checks with the command-line for systemd deployment
mcp-server-trento --enable-health-checkmcp-server-trento --enable-health-check --health-port 8080Testing Health Endpoints
# Test liveness endpoint
curl http://localhost:8080/livez
# Test readiness endpoint
curl http://localhost:8080/readyz
# Expected readiness response format:
# {"status":"up","checks":{"mcp-server":{"status":"up"},"api-server":{"status":"up"},"api-documentation":{"status":"up"}}}
# Expected liveness response format:
# {"status":"up"}Troubleshooting
This section provides solutions for common issues when deploying and using the Trento MCP Server.
Connection Issues
-
Trento MCP Server cannot connect to Trento API
-
Verify the
TRENTO_URLorOAS_PATHconfiguration points to accessible endpoints -
Check network connectivity between the Trento MCP Server and Trento components
-
Ensure API authentication is properly configured with valid tokens
-
-
MCP clients cannot connect to Trento MCP Server
-
Verify the Trento MCP Server is running and listening on the correct port (default: 5000)
-
Check firewall rules allow access to the Trento MCP Server port
-
Ensure the Trento MCP Server endpoint URL is correctly configured in client applications
-
Authentication Issues
-
API token authentication fails
-
Verify the Personal Access Token is valid and not expired
-
Ensure the token has the necessary permissions in Trento
-
Check that the
HEADER_NAMEconfiguration matches between server and client
-
-
Token not accepted
-
Confirm the token was generated from the correct Trento instance
-
Verify the token format and ensure it includes the "Bearer " prefix if required
-
Configuration Issues
-
OpenAPI specification not found
-
Check that
TRENTO_URLorOAS_PATHpoint to valid Trento API endpoints -
Verify the Trento Web and Trento Wanda services are running and accessible
-
Ensure autodiscovery paths are correct if using
TRENTO_URL
-
-
Tools not appearing in MCP clients
-
Check the
TAG_FILTERconfiguration - only operations with matching tags are exposed -
Verify the OpenAPI specifications are accessible and valid
-
Ensure the Trento MCP Server can parse the API documentation
-
Performance Issues
-
Slow response times
-
Check network latency between Trento MCP Server and Trento components
-
Review Trento API performance and database query times
-
Consider enabling debug logging to identify bottlenecks
-
-
High resource usage
-
Monitor Trento MCP Server memory and CPU usage
-
Check for memory leaks in long-running processes
-
Consider adjusting logging verbosity to reduce I/O overhead
-
Health Check Issues
-
Health checks failing
-
Verify health check endpoints are accessible
-
Check that all required services (Trento API, Trento MCP Server) are responding
-
Review health check configuration and timeouts
-
Logging and Debugging
-
Enable debug logging
-
Set
VERBOSITY=debugto get detailed logs -
Check Trento MCP Server logs for error messages and connection attempts
-
Review Trento component logs for API-related issues
-
-
Common log messages
-
"Failed to fetch OpenAPI specification" - Check API endpoint accessibility
-
"Authentication failed" - Verify API token configuration
-
"No tools available" - Check tag filtering and API documentation
-
Getting Help
If you continue to experience issues:
-
Check the Trento MCP Server logs for detailed error messages
-
Verify configuration values:
-
For systemd deployments, use
mcp-server-trento --help -
For Kubernetes deployments, run Helm with
--render-subchart-notesto view the rendered Trento MCP Server settings
-
-
Test API connectivity directly using curl or similar tools
-
Check the Trento server logs for API authentication and access issues
Using the Trento MCP Server
The Trento MCP Server provides the interface for AI-assisted infrastructure operations, enabling agentic assistants to integrate with Trento. By utilizing the Model Context Protocol, these assistants can perform monitoring and troubleshooting tasks through natural language. See MCPHost on SLES or Using alternative MCP clients for details.
Integrating the Trento MCP Server with MCPHost
This guide explains how to connect the Trento MCP Server to SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 16 using MCPHost, a lightweight CLI tool for the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
|
Supported only on SUSE Linux Enterprise Server for SAP applications 16.0 |
Prerequisites
-
An LLM provider and credentials.
-
Public hosted options, such as Google Gemini, OpenAI, etc.
-
Private/on-premises option, such as SUSE AI.
-
-
A running Trento Server installation with the Trento MCP Server component enabled.
-
A Trento Personal Access Token generated in Trento Web Profile view.
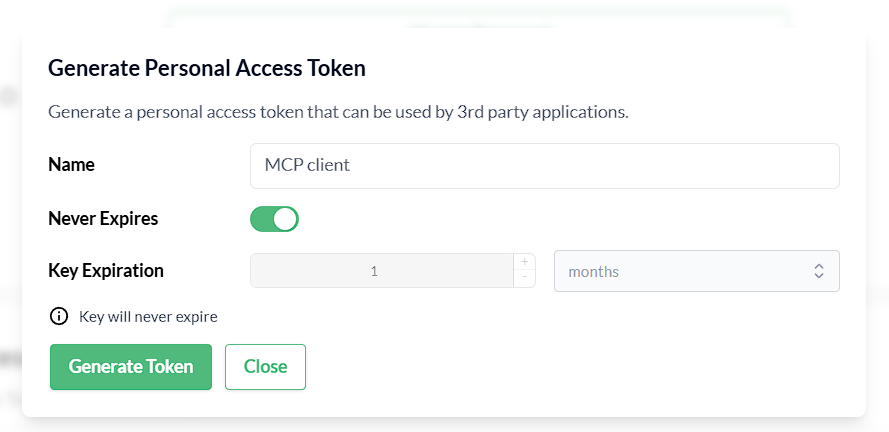 Figure 1. Generate a Personal Access Token in Trento
Figure 1. Generate a Personal Access Token in Trento
Install MCPHost
To install MCPHost, open a terminal and run the following commands:
sudo zypper refresh
sudo zypper install mcphostAfter installation, verify that MCPHost is available and working by checking its version:
mcphost --versionConfigure MCPHost
MCPHost reads its configuration from several locations; one common location is ~/.mcphost.yml. Create ~/.mcphost.yml with the following content:
mcpServers:
trento-mcp-server:
type: "remote"
url: https://trento.example.com/mcp-server-trento/mcp
headers:
- "Authorization: Bearer ${env://TRENTO_PAT}"-
Replace
https://trento.example.com/mcp-server-trento/mcpwith the actual URL where your Trento MCP Server is accessible:-
For Kubernetes deployments with ingress, use the ingress URL (e.g.,
https://trento.example.com/mcp-server-trento/mcp). -
For local or development setups, use
http://localhost:5000/mcp(adjust the port as needed). -
The transport type is configured on the Trento MCP Server, if using Server-Sent Events (SSE) transport instead of the default streamable transport, change the path from
/mcpto/sse.
-
-
If you configured a custom header name (using
HEADER_NAMEor--header-name), updateAuthorizationaccordingly.
|
Security best practice: Keep secrets out of configuration files. Store your keys in environment variables instead of hardcoding them. Export your keys in the shell before running MCPHost. For example: |
|
Configure remote LLM models directly in your MCPHost configuration. For example, to use Google Gemini as your model provider: |
Run MCPHost and use Trento tools
-
Start MCPHost:
mcphostIf no servers appear on startup, confirm your configuration file exists at
~/.mcphost.ymland that your environment variables are exported in the same shell session. -
Verify the connection to Trento and basic status:
/servers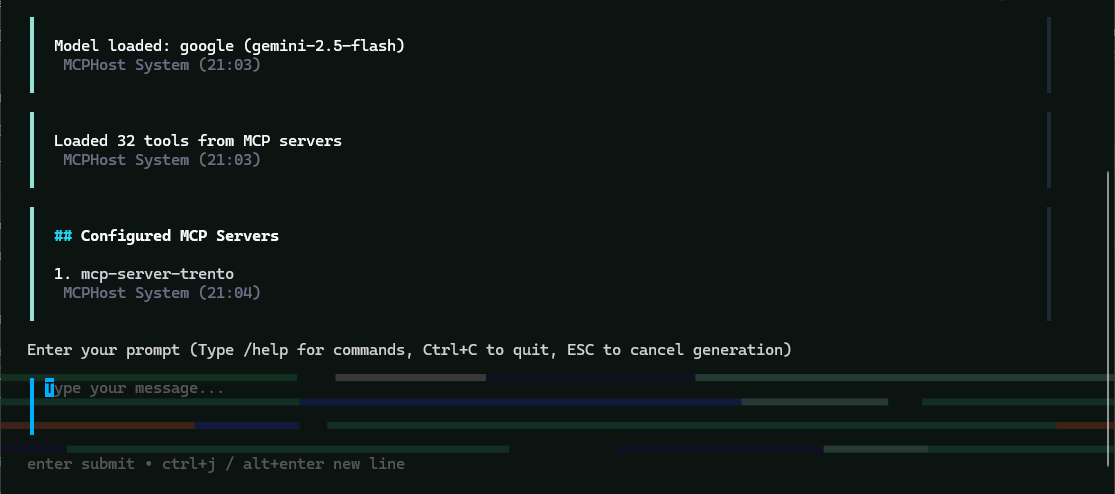 Figure 2. MCPHost initial screen with the Trento MCP Server connected
Figure 2. MCPHost initial screen with the Trento MCP Server connected
Use MCPHost to interact with Trento Server
-
"List all SAP systems managed".
-
"Show my HANA clusters".
-
"Are my SAP systems compliant?"
-
"What is the health status of my SAP landscape?"
-
"Show me all hosts running SAP applications".
-
"Are there any critical alerts I need to address?"
-
"Get details about the latest check execution results".
-
"Which SAP systems are currently running?"
Example MCPHost session querying Trento about SAP systems:
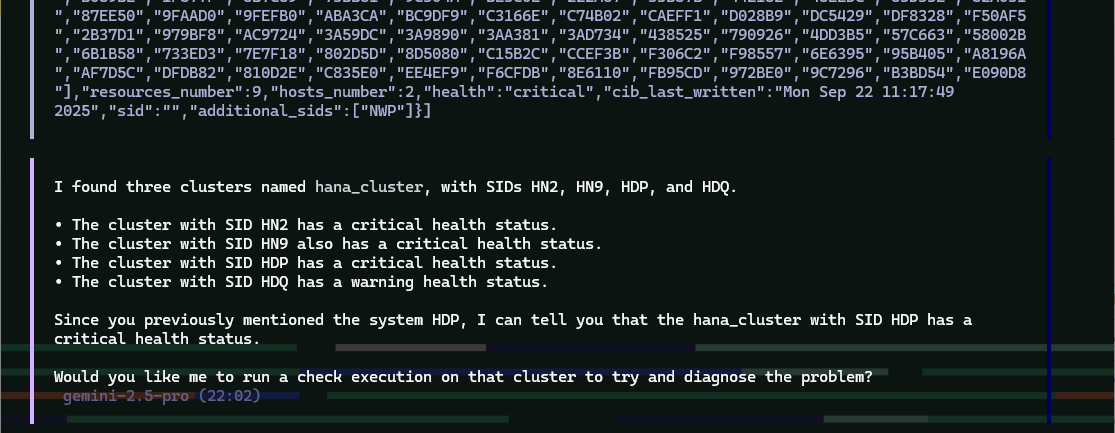
MCPHost Troubleshooting
If you encounter issues connecting MCPHost to the Trento MCP Server:
-
Connection errors
-
Verify that the Trento MCP Server URL in
~/.mcphost.ymlis correct and accessible from your system. -
Check if the Trento MCP Server is running by reviewing logs from your Trento installation.
-
Ensure network connectivity and that any required firewall rules are in place.
-
Test basic connectivity:
curl -I https://trento.example.com/mcp-server-trento/mcp.
-
-
Authentication errors
-
Verify that your personal access token is valid by testing it directly with your Trento Server API.
-
Ensure
TRENTO_PATis exported in the same shell session before runningmcphost. -
Check that the header name matches your server configuration (default:
Authorization). -
Ensure the token has the necessary permissions in Trento.
-
-
LLM provider errors
-
Verify that LLM
GOOGLE_API_KEY(or your provider’s API key) is exported correctly. -
Check the
provider-urlandmodelconfiguration in your~/.mcphost.yml. -
Confirm that your API key has sufficient quota and permissions with your provider.
-
-
General issues
-
Check the MCPHost terminal output for detailed error messages during startup or operation.
-
Review the Trento MCP Server logs for connection attempts and errors.
-
Verify that your configuration file exists at
~/.mcphost.ymland has correct YAML syntax.
-
Integrating the Trento MCP Server with other clients
The Trento MCP Server can be integrated with any client application that supports the Model Context Protocol. This makes it possible to interact with the Trento API and execute tools defined in the OpenAPI specification through your preferred AI assistant or development tool.
This guide uses Visual Studio Code with GitHub Copilot as an example, but the configuration procedures apply to any MCP-compatible client.
Prerequisites
-
An LLM provider and credentials.
-
Public hosted options, such as Google Gemini, OpenAI, etc.
-
Private/on-premises option, such as SUSE AI.
-
-
A running Trento Server installation with the Trento MCP Server component enabled.
-
A Trento Personal Access Token generated in Trento Web Profile view.
 Figure 3. Generate a Personal Access Token in Trento
Figure 3. Generate a Personal Access Token in Trento
Configuring your client
Once you have your Trento Server installation ready with the Trento MCP Server URL and API token, you can configure the MCP Server client. The examples below show JSON configuration format used by most MCP Server clients, including VS Code, Claude Desktop, and others.
Option 1: Configuration with prompted input
This configuration asks for your personal access token when the client starts, keeping credentials secure and out of configuration files. The password: true setting ensures your personal access token input is masked when you type it.
|
This option is supported by most clients, including VS Code. Check your client’s documentation if the prompt feature is not available. |
{
"servers": {
"trento": {
"type": "http",
"url": "https://trento.example.com/mcp-server-trento/mcp",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "${input:trento-personal-access-token}"
}
}
},
"inputs": [
{
"type": "promptString",
"id": "trento-personal-access-token",
"description": "Trento API key",
"password": true
}
]
}Option 2: Direct header configuration
For clients that don’t support prompted input, or for testing purposes, set your Trento personal access token directly in the configuration file.
|
When using this option, ensure your configuration file has appropriate permissions and is not committed to version control systems. |
{
"servers": {
"trento": {
"type": "http",
"url": "https://trento.example.com/mcp-server-trento/mcp",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "trento-personal-access-token"
}
}
}
}|
Replace |
Client options
For detailed guidance on taking advantage of MCP capabilities in different tools, refer to the following official documentation:
-
Visual Studio Code with GitHub Copilot - MCP Server Configuration.
-
Cursor - AI-powered code editor with MCP support.